Mazda 4 cylinder Engine History and Interchangeability Guide
Like most auto manufacturers Mazda has a lot of commonality between engines. There are four basic types of 4 cylinder piston motors that Mazda currently produces for the US market. They are grouped into engine families, ‘B’, ‘F’, 'Z' and ‘G’. The Miata uses the ‘B’ family of motors.
The ‘B’ family starts with a 1.3 liter SOHC. It was primarily used oversees but did come to the USA for a short stint in the Ford Festiva (other markets got a DOHC 1.3). The primary example of the early ‘B’ motors in the USA came here in the GLC as a 1.5 liter SOHC, later upped to 1.6 liters for the 323 in the mid 80’s (78x83.6mm). The 1.6 liter version has as large a bore as the block can accommodate and cannot really have it's displacement increased much more, in fact, enlarging the bore beyond +1mm is not advised. A DOHC head was designed for the 1.6 liter for the 1988 323 GTX turbo. Because of the severe duty that motor could see many enhancements were made to it for reliability reasons. A stronger web stiffened block and oil spray cooled pistons were among the changes. See SSS Automotive site from Australia for B6T tidbits.
The 116 HP Miata 1.6 DOHC motor from 1990-1993 is a normally aspirated version of that 323 turbo engine. It mainly differs from the turbo counterpart in higher compression pistons (to 9.4:1), lighter connecting rods and a lighter flywheel. This means that the NA version of the motor is quite over engineered for its applications. (how many NA motors do you know have oil spray cooling for the pistons). The automatic transmission version of the 1.6 DOHC engine has lower compression pistons to 9.0:1 and the camshafts have less duration. These changes were done for the automatic version to gain torque at a lower rpm and minimize detonation from the torque eating trans. The tradeoff is a less peak HP rating of 100. In 1991 a running change was made to the crank design from repeated failures of the pulley keyway. The pre-91 motors had a 22mm crank snout while the late 1991 and later had 27mm crank snouts. The 1.6 DOHC motor lived on in the Mercury Capri and XR2 until 1995.
The pistons that were available for the 1.6 B6P were the 323 GTX 7.8:1 with a heavy dish, the Miata automatic 9.0:1 with a moderate dish and the Miata 5-speed 9.4:1 with a shallow 1mm dish
The rods used in the 88-89 323GTX turbo are beefier. They have a thicker beam, thicker small end and larger size bolts. They weight approx 580 grams (w/bolts and nuts) vs the approx 540 grams of the Miata rod. The GTX rods are no longer available new from Mazda and the Miata pieces supercede it.
In 1994 the need to meet emissions standards and to confront cries for more power in the Miata was answered by using the 1.8 DOHC motor that has been in the Protege since 1990. It is also a ‘B’ family member but has a longer bore spacing to accommodate the larger 83mm pistons. The stroke was also increased to 85mm (both the 1.6 and 1.8 DOHC have the same 221.5mm block deck height and 134mm head height). The 1.8 is the same design and is just as robust as the 1.6. It has the same rods, same oil-cooled pistons, same oil passages, same head design, same HLA's and same crank design. Unlike the 1.6, the auto trans version of the 1.8 was not changed at all.
Since the 1.8 is really just a stretched 1.6, most everything on the front and back of the motor will interchange between the them. This includes the cam angle sensor, coolant intake pipes, flywheel/clutch assembly, various covers and brackets, cam gears, water pump, and timing belt tensioner, etc. The intake manifold, exhaust manifold, motor mount brackets and camshafts do not interchange because of the bore spacing differences. The 1.8 ‘B’ motor has also seen duty in the 1991-1995 Ford Escort GT/LXE, 1990-99 Mazda Protege, 1991-95 Mercury Tracer LTS and Kia Sephia GS. (FYI, the 90-93 Escort GT and Tracer LTS 1.8 DOHC use the same throttlebody and flowmeter as the 1.6 Miata).
A SOHC BP 1.8 was used in the Protege from 92-94 and the short block is identical to the DOHC. The SOHC pistons when used in a DOHC motor produce about 8.2:1 CR. The lower half of the SOHC two piece intake manifold also makes a great foundation for a custom IRTB for the 90-97 BP DOHC heads.
The head of the 1.8 ‘B’ was slightly revised with the stretch job by using larger sized intake and exhaust ports, larger valves, moving the cam angle sensor from the intake to the exhaust cam, and using a 4mm higher lift cam with shorter valve stem lengths and a larger base circle. OEM cams specs. For 1995 the valve springs were revised slightly stiffer. This allowed the thick seat shim (1+mm) that was used on the 94 1.8 motor to boost the installed spring pressure to be removed and was replaced by just a thin metal shim (about .005") to protect the head seat.
Starting with the 3/95 start of the ODB-II implementation (VIN 14193) the pistons were changed with a slight dome to increase the compression ratio to an actual 9.0:1. The '94-3/95 pistons were factory rated at 9.0:1 but actually was around 8.8.
The Japanese/Austr market version of the Protege got a turbo version of the 1.8, the 'BPT' equipped GTR and GTX. The very rare GTR recieved, amoung other things, a special web stiffened block cast 'BPII', a special cast '26' head with a flow vane in the intake port and sodium filled exhaust valves!.
In 1996 the peak HP rating of the Miata 1.8 motor was raised to 133 hp from 128. This comes primarily from the new for 1996 ODBII software having the ability to lean out the above 6000 rpm fuel curve. The slightly raised dome 9.0 pistons also continued.
The 1999-00 Miata uses basically the same 1.8 ‘B’ as the 1994-1997 but it was again revised. The 'BP-4W' engine uses a block with higher compression pistons to 9.5:1 from 9.0:1. The head had the most enhancements, the intake ports were raised from 39 degrees to 51 degrees to create a straighter flow path (the exhaust ports did not change), the hall effect cam angle sensor (CAS) was removed from the back of the head and replaced with a magnetic sensor and toothed wheel on the front of the crankshaft (a second magnetic sensor was added to the intake cam gear pulley to verify timing), and solid lifter camshafts with advanced timing, more duration and lots more intake lift were introduced.
The stock 99-00 cams are actually quite strong from the factory. They will easily support higher hp levels with more lift and duration than the 90-97 HLA cam. Mazda also makes an intake cam specifc to the home Japanese market. It has the same specs as the USA cam but the cam timing is advance a few degrees. If is part number BP5A12420, a Japanese spec cam identifed by "5A" cast into billet.
The 99-00 head will interchange onto the earlier 1.8 block if you also determine how to control the variable intake valve in the '99 manifold (VICS systems, probable a rpm activated selenoid will do it) as well as retrofit a cam angle sensor for the earlier ECU (the cam drive is still there so it just slaps on). You will also need a 99+ intake manifold.
To install 99-00 cams in an earlier head you just have to transfer the solid lifters. The early retainers, locks and springs can be used as-is. The lifters fit them fine. You just can't mix the locks and the retainers since the locks are different size. i.e. the 99+ locks must be used with the 99+ retainers and the 94-97 locks must be used with the 94-97 retainers. The only hard part is setting the lash. Using the 99+ cams in a M1 head requires using shims that are .020-.030" thicker since the cam basecircle and valve stem are slightly different. You will have to install the cams, measure the cold lash, and then order the required size shims. From the factory they come in 2.75mm - 3.75mm thickness about every .002 - .003" (~.05-.06mm)
 Spring retainer/lock compare 99+ left, HLA style right.
Spring retainer/lock compare 99+ left, HLA style right.
 99+ head uses blockoff plate for cam angle sensor. 99-00 identified by '4W' cast on head and cams.
99+ head uses blockoff plate for cam angle sensor. 99-00 identified by '4W' cast on head and cams.
 Interestingly though, the 99-00 EX cam retains cam angle drive.
Interestingly though, the 99-00 EX cam retains cam angle drive.
 99 intake ports are much higher and angle downward
99 intake ports are much higher and angle downward
 99+ intake port mismatch with 90-97 gasket.
99+ intake port mismatch with 90-97 gasket.
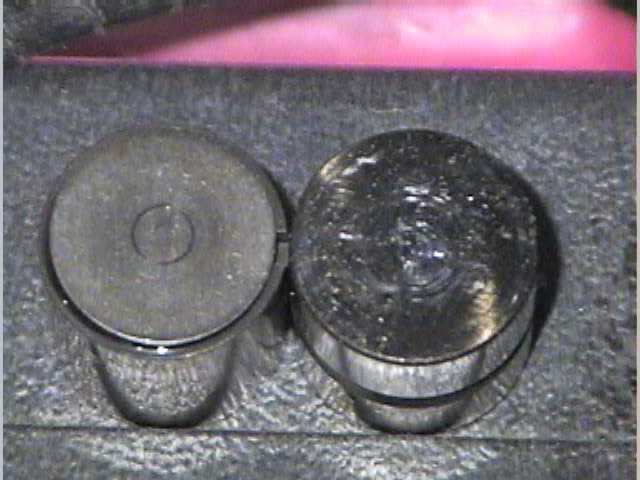

 99+ uses solid lifters (left) with adjustment disk while 90-97 uses HLA's (right).
99+ uses solid lifters (left) with adjustment disk while 90-97 uses HLA's (right).
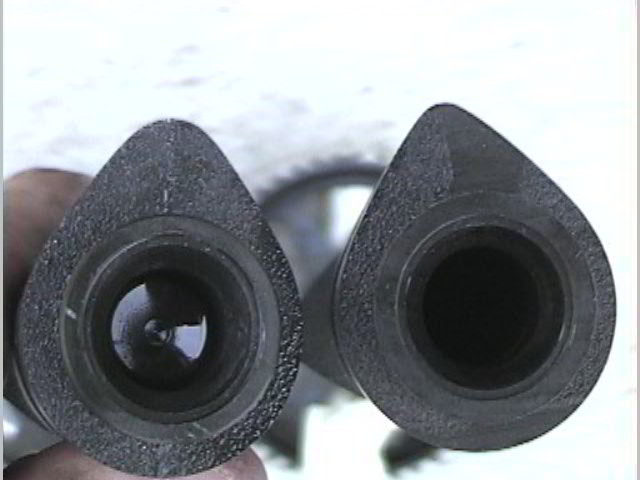 99 solid lifter intake cam vs 90-97 hydrallic, visible difference in profile. Mazda reverted back to the solid billet design from the 1.6 instead of the hollow design of the 90-97 1.8.
99 solid lifter intake cam vs 90-97 hydrallic, visible difference in profile. Mazda reverted back to the solid billet design from the 1.6 instead of the hollow design of the 90-97 1.8.
 99-00 uses a second timing sensor in the intake cam sprocket in addition to the crank sensor.
99-00 uses a second timing sensor in the intake cam sprocket in addition to the crank sensor.
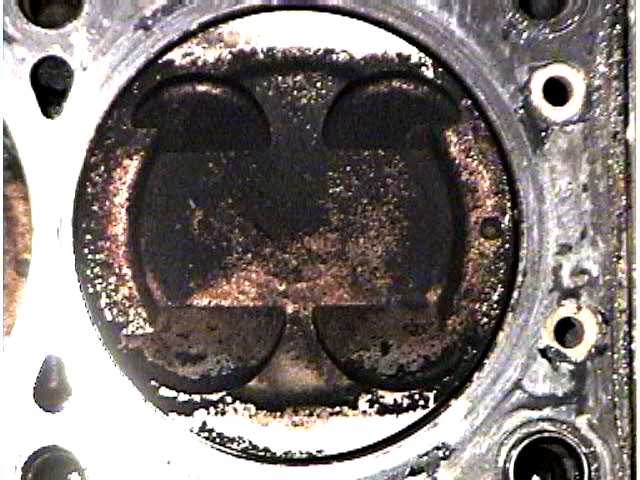 99-00 pistons produce 9.5:1 compression through a raised dome in the middle.
99-00 pistons produce 9.5:1 compression through a raised dome in the middle.
For 2001 Mazda introduced another variant of the 1.8 ‘B’ with 'VVT' variable valve timing and higher compression 10:1 pistons. It was advertised as having 155 hp but in reality only had 142 hp because of US emissions tuning. VVT is a hydralically adjusted intake cam for advance, retard and overlap and uses the oil pressure and a ECU controlled valve for adjustment.
The 2001 'BP-Z3' engine also had a new intake manifold without VICS but with a similar torque enhancing set of partial butterflys that increases velocity. One of the unique improvements for 2001 was the addition of a Main Bearing Support Plate (MBSP). Even though the 'B' engine uses 5 mail bearings the crankshaft can still flex quite a bit at higher revs and output levels. Mazda added a MBSP by tying the main caps together bolting it to a thicker stamping if the windage tray.
The 2001 'BP-Z3' engine's head can be retrofitted to ealier 1.8 blocks but you're on your own on how to control the cam selenoid. The MBSP can be installed on all prior 1.8 Miata blocks as long as the 2001 oil pan is used too - all year main caps come cast and machined with the bosses (it was actually OEM on the rare early GTR motor).
The 'Z' engines are a new family which is an evoltion of the 'B' engine. The head is entirely different with round ports and narrow valve angles but the shortblock is nearly the same as the B6.
The MX-5 got the MZR 2.0-liter engine for 2005. The engine is from the USA and used in the Mazda 6, is an all aluminum inline four-cylinder with 2.0 and 2.3 displacement variants. It is the same basic engine as the 2001 + Ford Ranger but with added balance shafts in the block and a performance head design (co-designed with Ford as a "world engine"). The MZR 2.0L has the same 86x86mm bore/stroke and the same bore spacing (although symetrical) of the FE3N engine (FE DOHC) but that is mostly coincidence and possibly to leverage some tooling reuse.
| Mazda 4 cylinder engines | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor | Years | Bore | Stroke | CC | Models |
| 1.3 B | 1988-1993(USA) | 71 | 83.6 | 1324 | Ford Festiva. Japanese market got DOHC head option. |
| 1.5 E/B5 SOHC | ? | 77 | 80 | 1490 | GLC |
| 1.6 SOHC B6 8V | ? | 78 | 83.6 | 1597 | 323, 90-92 Protege |
| 1.6 SOHC B6 16V | ? | 78 | 83.6 | 1597 | 92-93 MX-3 (16V SOHC head) |
| 1.6 DOHC B6P | 1988-1995 | 78 | 83.6 | 1597 | 323 GTX, Miata, Mercury Capri/XR2, 94-95 MX-3 |
| 1.8 SOHC B8 | 1990-1992 | 83 | 85 | 1839 | Protege |
| 1.8 DOHC BP | 1990-2001 | 83 | 85 | 1839 | 90-98 Protege, 91-96 Ford Escort GT, 94-01 Miata, Mercury Tracer LTS, 94-97 Kia Sephia GS |
| 2.0 F/MA | 1978-82 | 80 | 98 | 1970 | RWD 626, B2000, Courier |
| 2.0 FE | 1984-87 | 86 | 86 | 1998 | 8V FWD 626/MX6, B2000 |
| 2.0 FET | 1985-87 | 86 | 86 | 1998 | 8V FWD Turbo 626/MX6 |
| 2.0 FE3 DOHC | 1995+ | 86 | 86 | 1998 | Kia Sportage |
| 2.2 F2 | 1988-1992 | 86 | 94 | 2184 | 8V B2200, 12V FWD 626/MX6, Ford Probe |
| 2.2 F2T | 1988-1992 | 86 | 94 | 2184 | 12V FWD Turbo 626/MX6, Ford Probe |
| 2.0 DOHC FS * | 1993+ | 83 | 92 | 1991 | FWD 626/MX6, 1999+ Protege, Protege5 |
| 1.8 DOHC FP | 1999+ | 83 | 85 | 1839 | 1999 Protege |
| 1.5 ZL DOHC | 1999+ | 78 | 78.4 | 1498 | 1999+ Japanese market Protege. Has VVT |
| 1.5 Z5 DOHC | 1995-98 | 75.3 | 83.6 | 1489 | 1999 Protege |
| 1.6 Z6/M DOHC | 1999+ | 78 | 83.6 | 1597 | 1999+ Protege |